Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
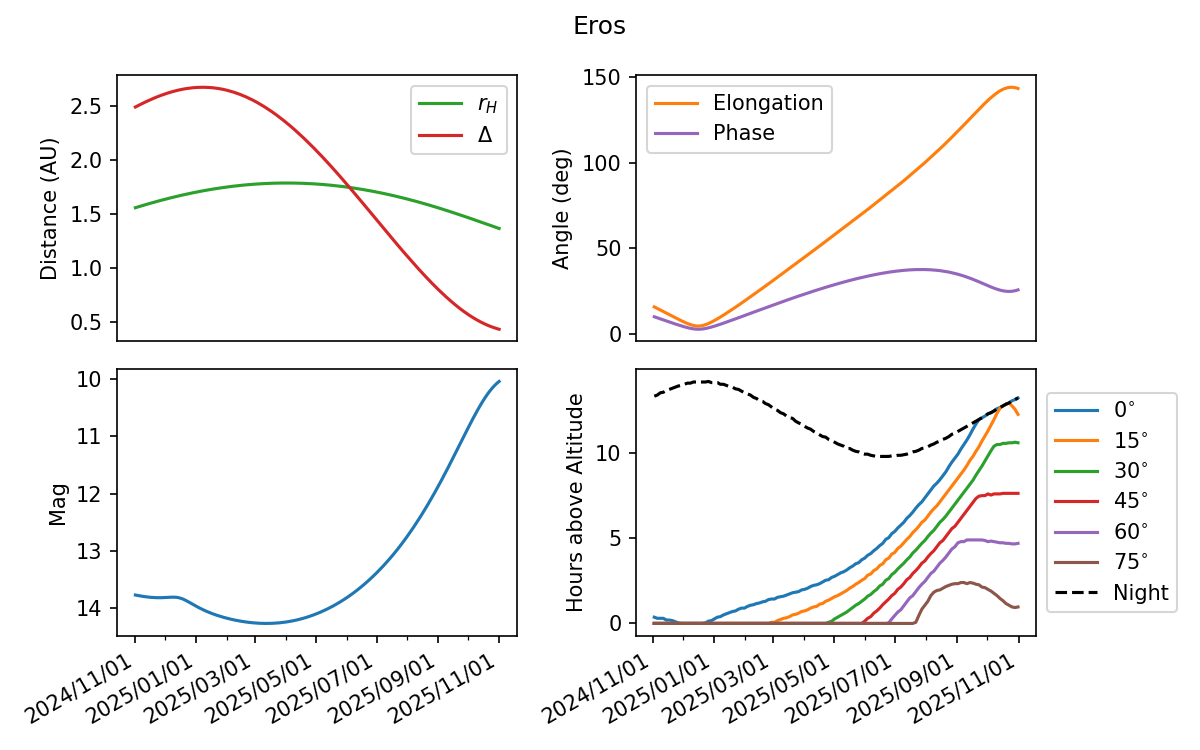
Plot observability of an object
Plot the observability of a given object from a position on the Earth.
- Given the following information:
Observers location on Earth.
Name of the object.
A start and stop date range.
This then plot various information about how observable the object is over the date range.
The first 3 plots are relatively self explanatory, the final of the plots is more complex. It plots the amount of time that the object is visible during the night. Specifically, it counts the total number of hours which the object is above the specified elevation. The dotted black line corresponds to the total length of the night as defined exactly sunset and sunrise at the observers location.
import kete
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.dates as mdates
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# Inputs:
# -------
obj = kete.HorizonsProperties.fetch("Eros", update_name=False)
start_time = kete.Time.from_ymd(2026, 11, 1).jd
end_time = kete.Time.from_ymd(2027, 11, 1).jd
# Observers position:
site = "Palomar Mountain"
# Calculate the values:
# ---------------------
def estimate_mag(states):
"""
Given a list of simultaneous states, estimate the apparent magnitudes of the object/
"""
obj = kete.horizons.fetch(states[0][0].desig, update_name=False)
h = obj.h_mag
g = obj.g_phase if obj.g_phase else 0.15
params = obj.json["phys_par"]
mks = []
for idx in [1, 2]:
for mk in "MK":
for param in params:
if param.get("name", "") == f"{mk}{idx}":
mks.append(float(param.get("value", np.nan)))
break
else:
mks.append(np.nan)
mk1 = mks[:2]
mk2 = mks[2:]
# if any mk values are defined, assume comet mags
# otherwise always compute using an H, even if H is nan.
if all(np.isnan(mks)):
mags = [
kete.flux.hg_apparent_mag(state[0].pos, state.fov.observer.pos, h, g)
for state in states
]
return {None: mags}
else:
mags = [
kete.flux.comet_apparent_mags(
state[0].pos, state.fov.observer.pos, mk1, mk2
)
for state in states
]
mags = np.array(mags).T
total_mags = mags[0]
nucl_mags = mags[1]
result = {}
result["Comet Mag (Total)"] = total_mags
if not all(np.isnan(nucl_mags)):
result["Comet Mag (Nucleus)"] = nucl_mags
return result
# Move times to the next solar noon for both start and end so that
# we land on noons when we step 1 day at a time later.
_, site_lon, *_ = kete.mpc.find_obs_code(site)
start_time = kete.time.next_solar_noon(start_time, site_lon)
end_time = kete.time.next_solar_noon(end_time, site_lon)
state = kete.propagate_n_body(obj.state, start_time)
times = np.arange(start_time, end_time, 1)
fovs = [
kete.OmniDirectionalFOV(kete.spice.mpc_code_to_ecliptic(site, jd)) for jd in times
]
vis = kete.fov_state_check([obj.state], fovs)
mags = estimate_mag(vis)
r_h = [state[0].pos.r for state in vis]
delta = [state.obs_vecs[0].r for state in vis]
phase = [state.phase_angles[0] for state in vis]
elong = [state.fov.observer.pos.angle_between(-state.obs_vecs[0]) for state in vis]
# For each day, step this frequently to compute the elevations and night durations
step_size = 3 / 60 / 24
elevations = []
night_durations = []
for day in times:
fovs = []
day_jds = np.arange(day, day + 1, step_size)
state = kete.propagate_n_body(state, day)
for jd in day_jds:
observer = kete.spice.mpc_code_to_ecliptic(site, jd)
zenith = kete.spice.mpc_code_to_ecliptic(site, jd, center="earth").pos
fovs.append(kete.ConeFOV(zenith, 180, observer))
day_vis = kete.fov_state_check([state], fovs)
day_sun_elev = [
90 - s.fov.pointing.angle_between(-s.fov.observer.pos) for s in day_vis
]
night_mask = np.array(day_sun_elev) < -3
night_duration = (max(day_jds[night_mask]) - min(day_jds[night_mask])) * 24
obj_elev = [
90 - state.fov.pointing.angle_between(state.obs_vecs[0]) for state in day_vis
]
obj_elev = np.array(obj_elev)
obj_elev[~night_mask] = 0.0
obj_elev[obj_elev < 0.0] = 0.0
night_durations.append(night_duration)
elevations.append(obj_elev)
elevations = np.array(elevations)
# Plot the results
# ----------------
dates = [kete.Time(t).to_datetime() for t in times]
plt.figure(dpi=150, figsize=(8, 5))
plt.suptitle(f"{obj.desig}")
plt.subplot(221)
plt.plot(dates, r_h, c="C2", label=r"$r_H$")
plt.plot(dates, delta, c="C3", label=r"$\Delta$")
plt.ylabel("Distance (AU)")
plt.legend()
plt.xticks([])
plt.subplot(222)
plt.plot(dates, elong, c="C1", label="Elongation")
plt.plot(dates, phase, c="C4", label="Phase")
plt.ylabel("Angle (deg)")
plt.legend()
plt.xticks([])
plt.subplot(223)
for mag_name, mags_vals in mags.items():
plt.plot(dates, mags_vals, label=mag_name)
if mag_name:
plt.legend()
plt.gca().invert_yaxis()
plt.ylabel("Mag")
plt.gca().xaxis.set_major_formatter(mdates.DateFormatter("%Y/%m/%d"))
plt.gcf().autofmt_xdate()
plt.gca().xaxis.set_major_locator(mdates.AutoDateLocator())
plt.gca().xaxis.set_minor_locator(mdates.MonthLocator())
plt.subplot(224)
plt.plot(dates, np.array(night_durations), ls="--", c="k", label="Night")
plt.plot(
dates,
[sum(np.array(a) > 0) * step_size * 24 for a in elevations],
label=r"Horizon",
c="k",
)
for ang in [20, 40, 60, 80]:
plt.plot(
dates,
[sum(np.array(a) > ang) * step_size * 24 for a in elevations],
label=f"{ang}" + r"$^{\circ}$",
)
plt.gca().legend(loc="center left", bbox_to_anchor=(1, 0.5))
plt.gca().xaxis.set_major_formatter(mdates.DateFormatter("%Y/%m/%d"))
plt.gca().xaxis.set_major_locator(mdates.AutoDateLocator())
plt.gca().xaxis.set_minor_locator(mdates.MonthLocator())
plt.gcf().autofmt_xdate()
plt.ylabel("Hours above Altitude")
plt.tight_layout()
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 4.230 seconds)